Are you a little lost among all the technical terms involved in sailing? It is essential to master all the nautical terminology in order to be well understood on board. Worry not, SamBoat has got you covered, and compiled a list of essential terms you should be aware of.
But before you start going through our glossary, we’ve put together some graphics to help you navigate your way around a boat even better.
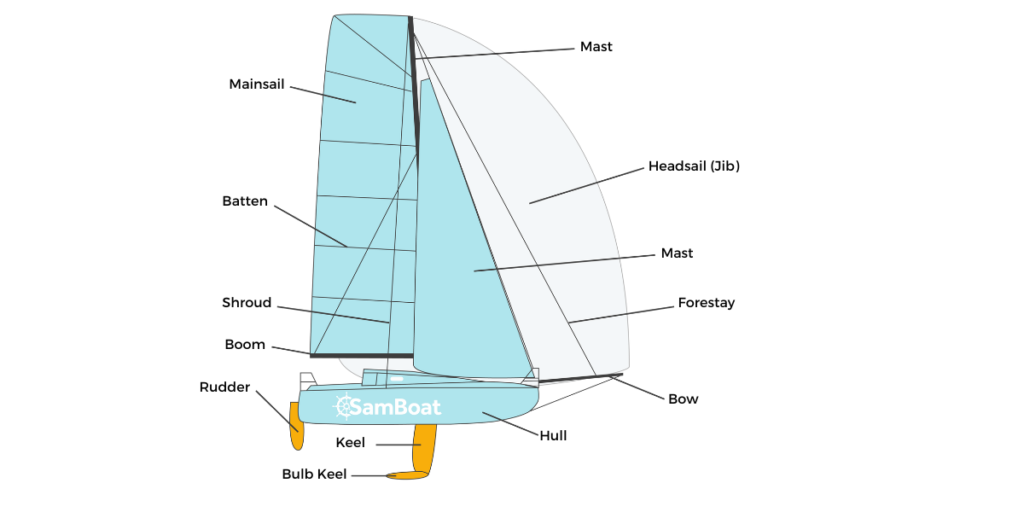
The different parts of a boat
For even more information on the different parts of a sailboat, check out this article.
Points of sail
The marine vocabulary
A
· Against: Placement of a sail or helm in the opposite direction
· Anchorage: Location or situation of a boat immobilised on its anchor. It also includes all the anchoring equipment.
· Antifouling: Paint designed to prevent marine organisms from clinging to the hull.
· Appendages: Submerged elements of the boat
· Ardent: Boat that has a natural tendency to rise with the wind
B
· Backstay: Part of the standing rigging supporting the mast on the stern.
· Balcony: Pailing used for safety on the boat
· Ballast: Large tanks installed at the bottom of a ship’s hold used to weigh down the boat
· Base: Submerged part of the transmission of an inboard or outboard motor supporting the propeller
· Battens: Rigid pieces inserted in the fabric of the sail to improve its profile.
· Beacher: Derived from the word Beach, which means to voluntarily run aground on the beach with one’s boat
· Boom: Horizontal support of the mainsail articulated on the mast
· Bottom boom: Hoist fixed between the hoist and the mast
· Boundary: Action of pulling on the sheet to close the angle of the mainsail
· Bow: Stop at the front of the hull
· Bowsprit: Extension at the front of the boat used to set a sail
· Bulb: Torpedo-shaped ballast at the bottom of the keel
· Bunk: A single berth on board a boat
· Bunkering: Movement of the boat that is luffing
· Bury: To drive the boat into the water by the bow
· Butt: All the ropes present on a ship
C
· Centerboard: The part of the boat underwater that exerts an anti-drift force to keep the boat from drifting.
· Chainplate: Metal part attached to the deck of the ship to which the cables holding the mast are connected.
· Channel: Navigable part of the river where boats must travel
· Cleat: A device on the boat that locks the ropes
· Cockpit: Space in the boat where the helmsman and crew usually sit
· Collision: A deliberate approach to a dock or floating object that creates a collision
· Compass: A type of marine compass that allows the user to determine the angle between the direction of the sighting and magnetic north.
· Course: Direction chosen
D
· Daggerboard well: On a dinghy, it is a place where the daggerboard can be inserted
· Deadweight: Anchor consisting of a surface buoy attached to the bottom by a chain to a heavy weight to which a boat can attach itself.
· Desalting: When the boat heels too much and turns over.
· Dinghy: Small unit aboard a larger boat that allows you to go ashore from your boat.
· Dropping: Action of lowering a sail
· Dyke: Artificial obstacle used to contain the water, on which the service or counter-haulage path is crested.
F
· Fender: Object suspended along the dock or the hull to absorb shocks and protect the hull
· Fittings: All the parts attached to the boat
· Floating anchor: Funnel of canvas struck at the end of a long line that is threaded onto the boat to make it drift in the wind bed.
· Foil: Wing shaped on one side of the boat that creates lift and allows the boat to fly over the water
· Forestay: Cable used to maintain the mast
G
· Gaff: A spar or long pole made of wood or aluminium, fitted with a hook, used in particular during manoeuvres to catch a mooring line or a buoy.
· Gennaker: Triangular downwind sail used between 90 and 120 degrees of the wind.
· Genoa: Large sail at the front of the boat generally used in calm seas.
H
· Halyard: Rope used to hoist or lower a sail.
· Heel: Inclination on the side of the boat under the effect of the wind due to poor weight balance
· Helm: Used to steer the boat by activating the rudder
· Hoist: Action of raising the sail
· Horn: Spar used to set a sail.
· Hull: Part of the hull under the boat.
I
· In board: Engine installed inside the hull of a boat
J
· Jib: Sail located at the front of the boat
· Jib: To pull down to turn the boat back to windward and change the side of the boat
K
· Keel: Fixed daggerboard under the boat used as a counterweight to prevent the boat from heeling.
· Knot: The knot is a unit of speed measurement used in marine (and air) navigation. One knot corresponds to one nautical mile per hour, or 1.852 kilometres per hour
L
· Leech: Upper part of the mainsail held by battens.
· Lifeline: Straps on the deck allowing one to attach oneself to avoid a bad fall
· Luff: To bring the axis of the boat closer to the wind
· Luffing: To tack upwind and to make a series of tacks to get upwind
M
· Mainsail: Main sail of the ship held between the boom and the mast.
N
· Nautical mile: Unit of measurement of distances at sea. One nautical mile represents 1.852 kilometres.
· Nose: A self-contained tank for outboard motors.
· Outboard: Engine mounted on the transom of a boat. It is by definition easier to mount and dismount than an inboard engine.
P
· Pitch: Angle of the boat in relation to the wind
· Plug: Angle given to the hull
· Port: The left side of a boat when looking at the bow
· Porthole: Glass opening in the hull
· Provisioning: All the provisions carried on board a ship
Q
· Quest: Angle less than 90° formed by the mast and the waterline. In the longitudinal plane of the sailboat, it is the angle of inclination of the mast towards its stern (positive rake) or more rarely towards the bow (negative rake)
R
· Reefing: System allowing to reduce the surface of the mainsail in the breeze
· Reminder: The crew is on the opposite side of the boat to avoid heeling.
· Roll: Lateral movement of the boat from port to starboard under the effect of the swell.
· Deck: Construction on the deck of a boat that allows protection and visibility
· Rudder: Submerged and rotating part that allows the boat to be steered
S
· Scull: An oar that is handled from the stern of the boat, making a figure-of-eight motion. The scull allows a single sailor to move a boat.
· Setting a course: To stop the boat facing the wind
· Setting sail: To leave, to set sail
· Sheet: End used to adjust the angle of a sail in relation to the wind.
· Shelter: A place where the vessel can easily find refuge in case of difficulty
· Shrouds: Metal cables that hold the mast laterally
· Soft: A boat with a natural tendency to move away from the wind.
· Sounder: Instrument used to determine the height of water under the boat at a given time
· Spar: Non-generic term that designates the different elements of the rigging
· Spinnaker: Large sail launched at the front of the boat
· Spinneret: Steel cable passing through the stanchions to avoid falling into the water
· Splice: To braid a rope
· Stanchion: Vertical supports placed outside the boat to prevent it from falling
· Starboard: The right side of a boat when looking at the boat from the front
· Stern: Rear part of the boat
· Strike: To manoeuvre the boat away from the wind
· Sunbath: Mattress attached to a front or back deck of a boat
T
· Tack: Side of the boat on which the wind blows
· Tacking: Turning the boat so that the wind comes from the other side of the boat
· Tonnage: Rules defining the characteristics of the boat to be respected if the boat is to participate in competitions
· Upwind: Point of sail that allows the boat to sail as close as possible to the wind.
V
· vhf: Abbreviation for Very High Frequency. Name given to a communication system that uses VHF and is particularly suited to coastal navigation
W
· Winch: A device that makes it easier to trim sails
· Windvane: A plate that moves around a vertical axis to indicate the direction of the wind received by a sailboat. The wind vane is placed at the top of the mast.
For further reading, you can check out our article on some of the more colloquial sailing terms you need to know.



